When configuring e-mail on a new device, you’ve probably noticed two options: POP3 and IMAP. The option you choose dictates whether your email remains in sync across your phone, tablet, and computer or is accessible only on one device.
POP3 and IMAP are email protocols that allow your email client setup based on different email platforms like Outlook, Gmail or Apple Mail to communicate with the mail server. In a nutshell, these two options determine whether your emails are saved on a mail server or downloaded to your device.
In this blog, we’ll discuss IMAP and POP3 separately, explain their differences, and outline the advantages and disadvantages. By the end of this blog, you will have a clear insight about when to use each protocol and which one is suitable for you.
Related Read: Webmail Port Numbers Explained: IMAP, POP3, and SMTP Ports
Table Of Content
What is POP3? (Post Office Protocol 3)
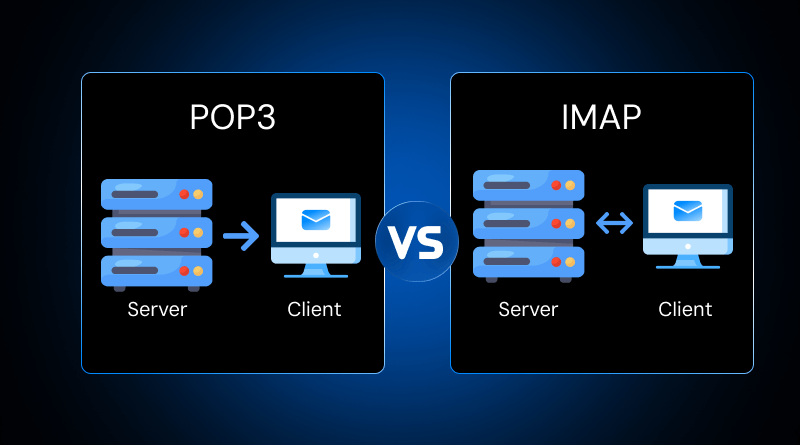
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) can be likened to a system with a physical post office. Visualize yourself going to the post office to pick up your letters and bringing them home. Once you’ve received them, the post office does not have a copy; everything is in your possession. The same idea applies to emails when you use POP3. Emails are downloaded from the email server and stored on a device; as set, they are removed from the server.
POP3 protocols work on the principle of downloading messages on a single device. From the device on which the emails are downloaded, they will not be stored on any other server or device. These downloaded emails will not be stored on any other server or device and hence will be treated as stored remotely. While certain email client setups offer the ability to keep emails on the server, with POP3, the emails are downloaded and stored remotely. They will not be kept on the email server.
POP3: Pros and Cons
POP3 is probably the best email protocol option for someone who only operates out of one device, wants to access their emails offline, and wishes to limit server storage vs local storage. However, in the modern age with so many devices available, the restrictions of POP3 are often considered a dealbreaker.
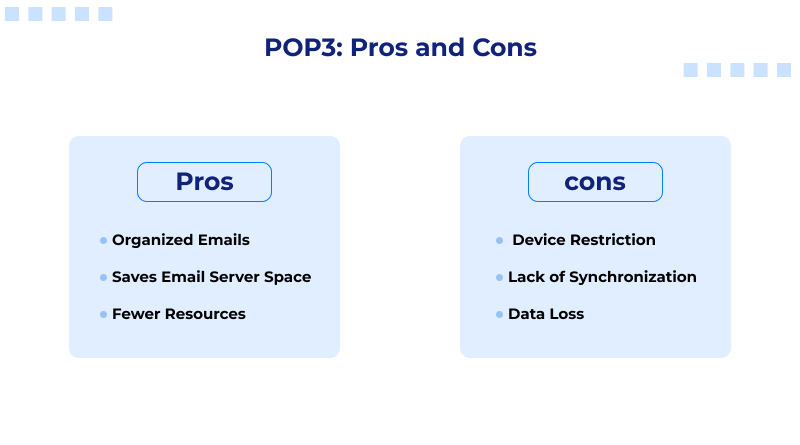
Pros
- Organized emails: POP3 will help you to organize emails that you have to respond to, as an internet connection is not needed to reply to the emails.
- Saving Email Server Space: POP3 is beneficial as it removes emails stored on the server after downloading, which is particularly useful when server space is low.
- Fewer Resources: POP3 is great to use, as the protocols are light, as it only requires a single server to relocate emails. Thus, it is a quicker email protocol to accommodate.
Cons
- Device Restriction: POP3 is restrictive, as the emails can only be downloaded on a single device, which, for numerous people, will be inconvenient, as multiple device access is required.
- Lack of Synchronization: POP3 is inefficient, as it does not take other devices into consideration. Any emails that are deleted or moved are all stored on a single device.
- Data Loss: POP3 is suboptimal, as during a device crash, all emails will be lost, as no backup was stored, and devices will only function as a single unit.
What is IMAP? (Internet Message Access Protocol)
IMAP, like cloud services, is for emails. Imagine you keep your files in a cloud folder. You can access and modify it from your computer, phone, or tablet. Any adjustment from any device is available on all devices. IMAP does the same with emails.
IMAP does not download your emails to a device. The emails stay on a mail server. They are available on all devices you use to access your account. When you delete an email from your phone, it also disappears from your laptop, tablet, and webmail. The server acts as a centralized system. You do not have to worry that your inbox changes between devices.
IMAP: Pros and Cons
IMAP is preferred by users who access their email on many devices. It offers real-time synchronization. IMAP provides flexibility and reliability. The downsides are a lack of server, storage, and internet connection.
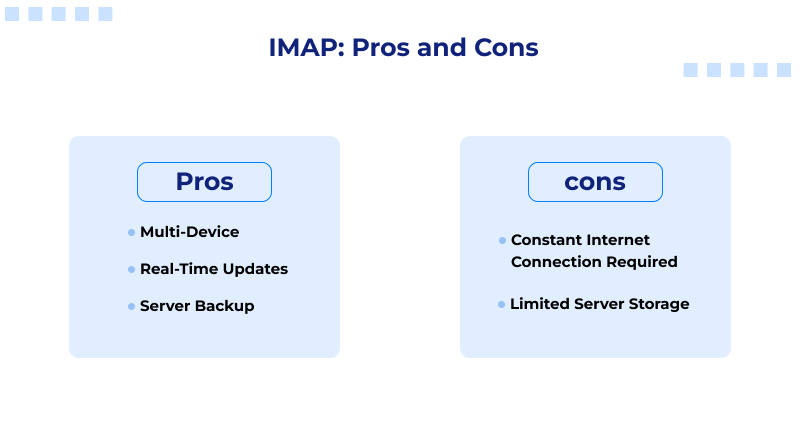
Pros
- Multi-Device: IMAP is ideal for the modern interconnected world, as it gives you the same inbox no matter what device you use.
- Real-Time Updates: Whatever action you perform, such as reading, moving or deleting an email, it reflects instantly on all devices associated with your account.
- Server Backup: You do not lose your emails even when your device is lost, stolen or damaged, since the emails are still on the server. Many providers also back up their servers, which offers additional protection.
Cons
- Requires Constant Internet Connection: Unlike POP3, there is no complete offline access. You cannot effectively read and manage emails without an adequate connection.
- Server Storage is Limited: Since emails and attachments are stored on the server, it can become full, which is particularly the case with email accounts that receive a high number of emails with large files attached.
POP3 vs. IMAP: A Direct Comparison
Choosing between POP3 and IMAP can often be based on personal preference and usage style. POP3 is straightforward and very easy to use for people who check their mail on one computer and would like offline access to their emails while also saving server space. IMAP is for real-time sync and access on multiple devices and is useful for phone, computer, and tablet users.
The simplest way to compare POP3 and IMAP is to put them side by side.
| Feature | POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) | IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) |
| Storage Location | Local device (downloads emails) | Server (emails remain stored on the server) |
| Multi-Device Access | Tied to one device | Accessible on multiple devices |
| Synchronization | One-way download only | Two-way sync between server & devices |
| Server Storage Impact | Reduces storage (emails removed from server) | Consumes storage (emails stay on server) |
| Best For | Single-device users, limited storage, offline access | Multi-device users, real-time syncing, flexibility |
IMAP or POP3 for Gmail and Outlook: Which Do You Like Better?
Both Gmail and Outlook have IMAP as the preferred option over POP3. This is because most people nowadays access their email on more than one device. Data from Google shows that more than 75% of Gmail users access their email from multiple devices; therefore, synchronization is essential. IMAP works best, as all actions of reading, deleting, and moving emails to other folders are done consistently across all platforms – webmail, mobile, and desktop apps.
Outlook users prefer IMAP as well. Microsoft’s data shows that nearly 60% of the connections in Outlook clients are tied to IMAP accounts because users need real-time synchronization between their PCs and mobile devices. In single-device setups, users have access to POP3. However, it is becoming obsolete in the business world.
To summarize, if you are searching for “Gmail IMAP or POP3” and “POP3 vs. IMAP for Outlook,” the data is clear – IMAP is the preferred protocol for multi-device, cloud-first email management.
Your preferred access and management style is why you would choose POP3 over IMAP. POP3, an email protocol, is designed to ensure that emails can be accessed, worst case offline, by downloading them to one device. This is useful for people who intend to work on a computer most of the time. In contrast, IMAP allows access to real-time emails on all computers, tablets, and cell phones.
It also has flexibility, making it a preferred option over POP3 if you are a modern user. Ultimately, the IMAP option is the geared option for most users in the current world who are living in modern times. In case one device is in use and there is an interest to use server space, offline access could use POP3.
All emails should work seamlessly with reliable hosting providers, which is why hosting providers such as MilesWeb ensure their email hosting services provide both email protocol (POP3 and IMAP) options. Make sure your email exchange communication runs smoothly, whether you choose the handy mobility of IMAP or POP3’s streamlined simplicity.
FAQs
1. Which email protocol is better for accessing my email from multiple devices?
For customers who use multiple devices, such as a smartphone, a tablet, and a laptop, IMAP is the better choice, as it keeps all emails stored on the server and makes sure any changes that are made are synchronized across all devices. Unlike IMAP, POP3 can only be accessed through one device and does not synchronize emails.
2. Which email protocol is better for checking new mail?
For initial downloads, POP3 can be a tad faster as it pulls messages from the server and places them on your device. IMAP, on the other hand, is much smoother, as it syncs emails in real time, making it much more efficient for active users who switch between devices.
3. What are the differences between email synchronization using POP3 and using IMAP?
In POP3, synchronization does not exist—it is a one-way process where emails are downloaded, and the emails are usually deleted from the server. IMAP employs a two-way sync, so any changes (read, delete, or move) made on a device are reflected on the server and visible on all other devices.
Which is more efficient to use for an email account with large emails and limited server space?
For accounts with strict storage limits, POP3 is more efficient, as it transfers the emails stored on the server and deletes them to the devices, freeing server space. However, with modern email services like Gmail and Outlook, which have larger storage systems, IMAP is more efficient, as it supplies hassle-free access from multiple devices, which saves space.