N8N is an effective open-source application created to automate workflows. It helps you connect with and automate with multiple devices. MilesWebs n8n VPS has a pre-installed tool, that is already installed with the Docker environment. This ensures that you get a fast and simple deployment of your automation workflow. This guide will take you through the process of accessing, configuring and managing your n8n.
- Gaining access to the web interface
- Point your web browser to https://n8n.[your-vps-hostname].
- The first time you log in, an admin account will be created.
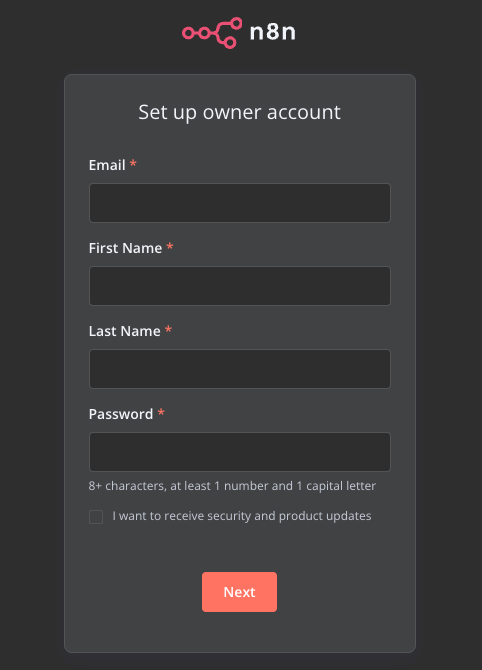
Building Workflows
Creating workflows in n8n is a visual and intuitive process. Click “New Workflow” button in the dashboard. You can begin your automation task on a blank canvas that appears after clicking. In n8n, Nodes are small task blocks. Each block represents tasks like data retrieval from an API, sending email, or information processing.
To build a workflow, just drag and drop nodes to the canvas. But remember every node requires configuration to define its functionality. To open a node’s settings, click on it. With an HTTP Request node, you can specify details such as the request URL, method (GET, POST, etc.), and any necessary parameters. Connecting nodes by dragging their outputs to their inputs establishes the sequence of events.
When you have linked your nodes, press the button that says ‘Execute Workflow’ to test the workflow. The results will be continuously shown on all connected nodes so that you can debug and optimize your automation.
Create automation in the work by introducing a trigger node. The Trigger nodes involve the use of the node referred to as the Cron node to execute tasks on a scheduled basis or the use of the Webhook type node to act as a response to external events. When you finish your workflow save it so it will last in your n8n instance.
Updating n8n
Updating n8n is crucial for your streamlined workflow. It helps get you the latest features and fixes. Follow these steps in SSH to update n8n:
# Pull latest version
docker compose pull
# Stop and remove older version
docker compose down
# Start the container
docker compose up –dQueue mode
n8n queue mode improves the performance and scalability because the workflow processing is asynchronous (via a message queue system (Redis)). Workflows do not run as soon as they are executed but rather are queued and run in distinct worker nodes; a feature that permits improved load balancing, fault tolerance, and parallel running of multiple workflow instances. This comes in handy, especially in managing a large workflow.
In case you select to use “Ubuntu 24.04 with n8n (queue mode)”, by default, it will be configured to run with 3 workers. To magnify this value, the following must be implemented:
docker compose up -d --scale n8n-worker=<number>Environment variables
While you deploy MilesWeb’s Ubuntu 24.04 with the n8n tool, each n8n setting is handled as Docker. It is done through an environment variable declared in the Compose files launching the container.
SSH to your VPS and edit the file which is placed at /root/docker-compose.yml. An environment block is located under the n8n section. In each of the lines, the pattern used comes out as VARIABLE_NAME=value.
Add and modify your variables to that list of environments. Save as file, in the same /root folder, and run docker compose up -d. Docker makes the n8n service appear and disappear again gracefully in order to allow the new variables to take effect.
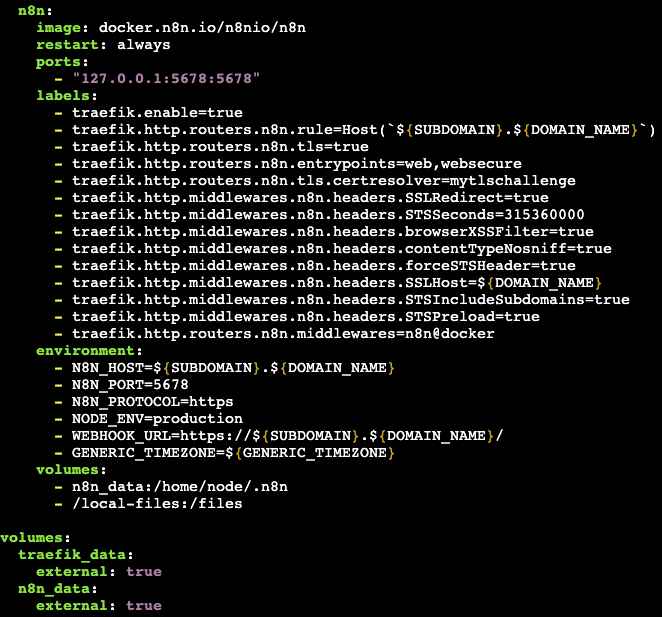
You can put the password or any other secret key in a special file named.env (in the same folder) and then add them in the docker-compose.yml with ${SECRET_NAME}. Docker Compose replaces them automatically and your secrets do not appear in the file that you might want to share later.